Matematické Fórum
Nevíte-li si rady s jakýmkoliv matematickým problémem, toto místo je pro vás jako dělané.
Nástěnka
❗22. 8. 2021 (L) Přecházíme zpět na doménu forum.matweb.cz!
❗04.11.2016 (Jel.) Čtete, prosím, před vložení dotazu, děkuji!
❗23.10.2013 (Jel.) Zkuste před zadáním dotazu použít některý z online-nástrojů, konzultovat použití můžete v sekci CAS.
Nejste přihlášen(a). Přihlásit
#1 18. 04. 2019 13:46
- stuart clark

- Příspěvky: 1015
- Reputace: 7
limit
If 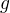 is an continuous periodic and bounded function with period
is an continuous periodic and bounded function with period  such that
such that 
let  and
and 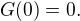 Then
Then  is
is
Offline
- (téma jako vyřešené označil(a) byk7)