Matematické Fórum
Nevíte-li si rady s jakýmkoliv matematickým problémem, toto místo je pro vás jako dělané.
Nástěnka
❗22. 8. 2021 (L) Přecházíme zpět na doménu forum.matweb.cz!
❗04.11.2016 (Jel.) Čtete, prosím, před vložení dotazu, děkuji!
❗23.10.2013 (Jel.) Zkuste před zadáním dotazu použít některý z online-nástrojů, konzultovat použití můžete v sekci CAS.
Nejste přihlášen(a). Přihlásit
#1 04. 05. 2019 09:51 — Editoval stuart clark (04. 05. 2019 09:51)
- stuart clark

- Příspěvky: 1015
- Reputace: 7
function
Consider the polynomial 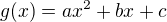 and
and 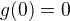 and
and 
Then minimum value of 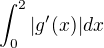 is
is
Offline
#2 05. 05. 2019 09:55
- stuart clark

- Příspěvky: 1015
- Reputace: 7
Re: function
From 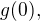 we have
we have 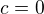 and from
and from 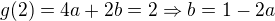
So  and
and 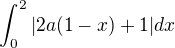
Put 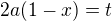 and
and 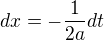
we have 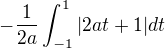
How i solve it please explain. Thanks
Offline
#3 05. 05. 2019 12:59
Re: function
Let's start from the integral 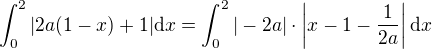
apparently,
now you should discuss three cases
- 1+1/(2a) < 0,
- 0 ≤ 1+1/(2a) ≤ 2,
- 2 < 1+1/(2a),
compute the definite integrals, which give you some functions depending on 'a'.
Maximize them and choose the largest value.
Příspěvky psané červenou barvou jsou moderátorské, šedá je offtopic.
Offline
#4 05. 05. 2019 17:00
Re: function
↑ stuart clark:
Hi Stuart Clark
g(0)=0 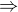 c=0
c=0
g(2)=0 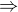
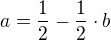

a)If b<1 then the function is growing.
If b<1 and b>0 then we calculate the area of trapezoid 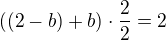
If b<1 and b<0 then we calculate the area of two triangles

If  then the area is
then the area is 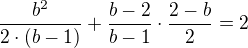
The situation  is not possible (b<1 & b>2)
is not possible (b<1 & b>2)
b)If b>1 then the function is declining
There is the similar situation as in a).
If  you will get the same trapezoid.
you will get the same trapezoid.
If  you will get the same triangles.
you will get the same triangles.
c) If b=1 the function is constant I=2
tg(x) je funkcí života.Jednou jsi nahoře🗽, podruhé zas dole 🗿.
Offline
#5 06. 05. 2019 08:37 — Editoval stuart clark (06. 05. 2019 08:38)
- stuart clark

- Příspěvky: 1015
- Reputace: 7
Re: function
Thanks ↑ byk7: and ↑ krakonoš:.
Can we solve this way
Equality hold when 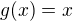
Offline